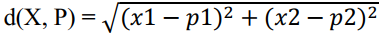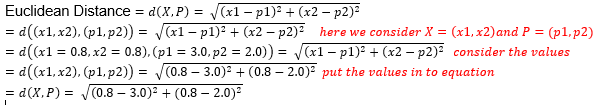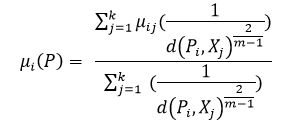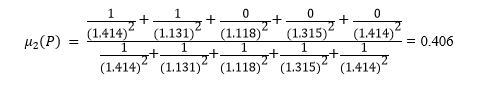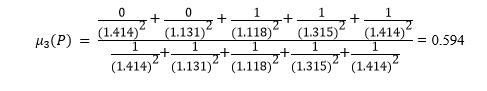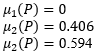Fuzzy K-Nearest Neighbor (FKNN)
Introduction to Fuzzy k-NN:
In the area of research and application, classification of objects are important. k-nearest neighbor algorithm (k-NN) is a non-parametric method used for classification and regression. In both cases, the input consists of the k closest training examples in the feature space. The output depends on whether k-NN is used for classification or regression. The theory of fuzzy sets is introduced into the k-nearest Neighbor technique to develop a fuzzy version of the algorithm. Three Methods of assigning fuzzy memberships to the labeled samples are proposed, and experimental results and comparisons to the crisp version are presented. In fact, not only does the fuzzy algorithm dominate its counterpart in terms of a lower error rate, the resulting memberships give a confidence measure of the classification. The fuzzy k-NN rule is also shown to compare well against other standard, more-sophisticated pattern recognition procedures in these experiments. A fuzzy analog of the nearest Prototype algorithm is also developed.
Let’s understand fuzzy k-NN in mathematical way:
Consider we have data sets with classes.
| Data set | Class | Data set | Class | Data set | Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 = (0.8, 0.8) | 1 | X2 = (1.0, 1.0) | 1 | X3 = (1.2, 0.8) | 1 |
| X4 = (0.8, 1.2) | 1 | X5 = (1.2, 1.2) | 1 | X6 = (4.0, 3.0) | 2 |
| X7 = (3.8, 2.8) | 2 | X8 = (4.2, 2.8) | 2 | X9 = (3.8, 3.2) | 2 |
| X10 = (4.2, 3.2) | 2 | X11 = (4.4, 2.8) | 2 | X12 = (4.4, 3.2) | 2 |
| X13 = (3.2, 0.4) | 3 | X14 = (3.2, 0.7) | 3 | X15 = (3.8, 0.5) | 3 |
| X16 = (3.5, 1.0) | 3 | X17 = (4.0, 1.0) | 3 | X18 = (4.0, 0.7) | 3 |
There are three classes and they are 1, 2, 3. We consider test pattern P = (3.0, 2.0) and k = 5.
Now calculate the distance between X and P using Euclidean Distance. Here X represents all the data sets from data sheets X1, X2, X3…. X18. P represents the test pattern and k = 5 stands for 5 nearest neighbors.
Euclidean Distance
.
Now, if I write the third formula using data sets and test patterns, it will be looking like this.
Euclidean Distance =
I wish after using the data sets X and test pattern P, someone will not actually understand what’s going on in the formula. Then let’s try with the values of X and P. Here, for the value of X, I use the values of X1(0.8, 0.8) from the data sheet and for the value of P (test pattern), use P(3.0, 2.0).
I wish it’s now understandable for everyone. Now, dig into the mathematics and let’s see test pattern P(3.0, 2.0) belongs to which class. In this example, we have only three classes and they are 1, 2, and 3.
Let’s find the distance between X and P and find the five lowest results because k = 5
Here the list of five lowest results with their class after calculating the distance between X and P. As we consider k = 5 then the nearest neighbor are given below in the list.
| 1st lowest | Class | 2nd lowest | Class | 3rd lowest | Class | 4th lowest | Class | 5th lowest | Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X16 = 1.12 | 3 | X7 = 1.13 | 2 | X14 = 1.31 | 3 | X6 = 1.41 | 2 | X17 = 1.41 | 3 |
Now we consider that,
Class 1 = 0, (Class 1 has no members)
Class 2 = 2, (Class 2 has 2 members and they are X6, X7),
Class 3 = 3, (Class 3 has 3 members and they are X14, X16, X17).
After finishing all the calculation from above, we consider the test pattern P= (3.0, 2.0) and k = 5 then nearest patterns are X16, X7, X14, X6 and X17.
The formula for the calculation is,
Here, I consider m = 2. We can assign any kinds of value to m. So, as I choose m = 2, then
We know Class 1 has no patterns like X1, X2, X16 then we consider 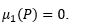
For Class 2, we consider 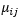
For Class 3, we consider 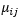
Calculation for Class 2 applying values of X6, X7, X16, X14 and X7:
Calculation for Class 2 applying values of X6, X7, X16, X14 and X7:
So,
If we choose a maximum result from three classes, then test pattern P (3.0, 2.0) belongs to class 3.
There is a link of a paper on Fuzzy k-NN. You can read this paper for further knowledge. [A Fuzzy K-Nearest Neighbor]
You can also go to this page to find codes for matlab. https://ww2.mathworks.cn/matlabcentral/fileexchange/21326-fuzzy-k-nn