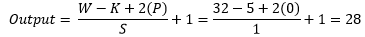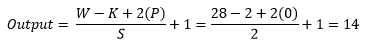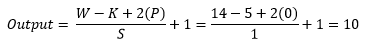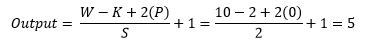Break Down Lenet-4
Introduction:
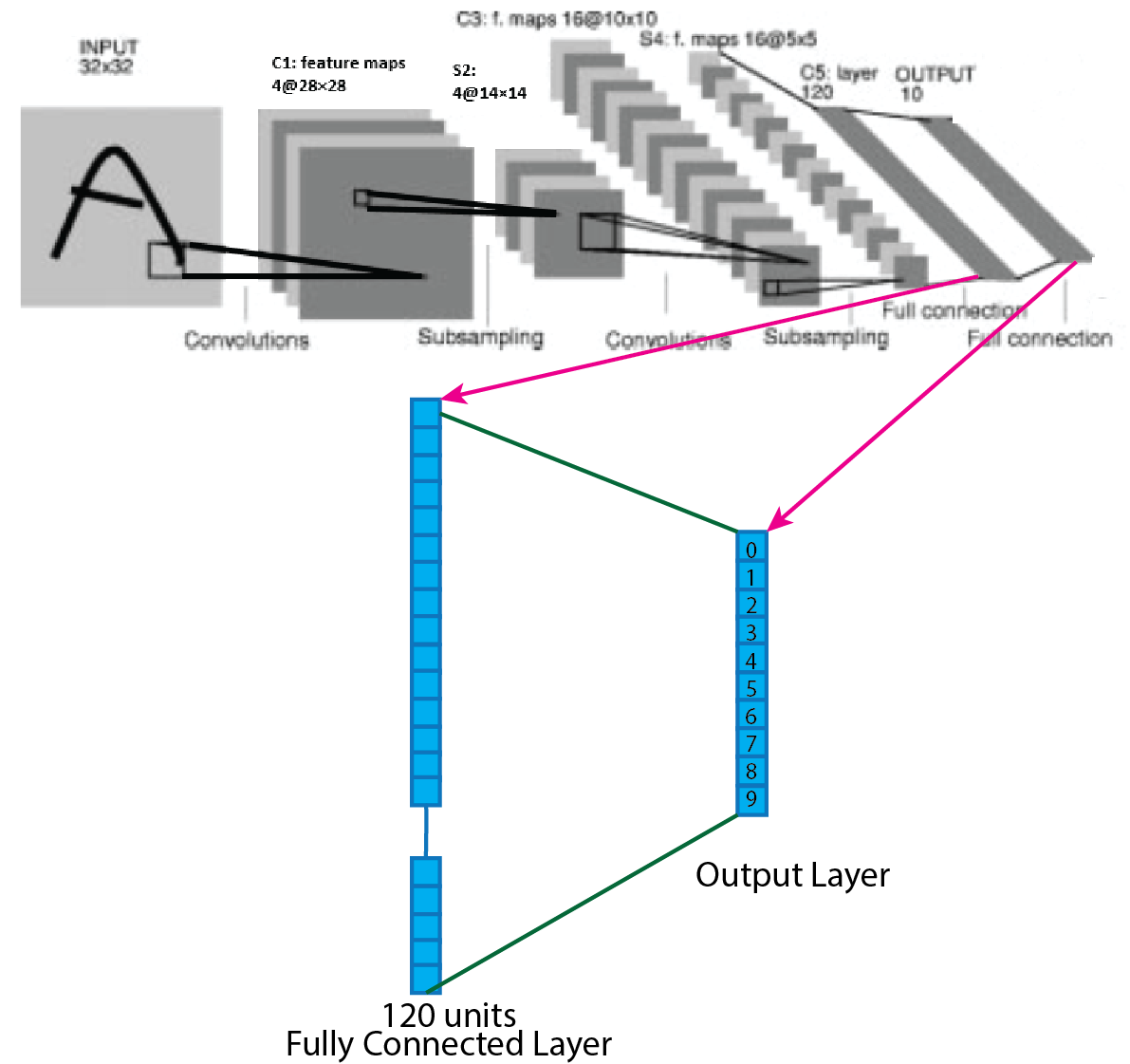
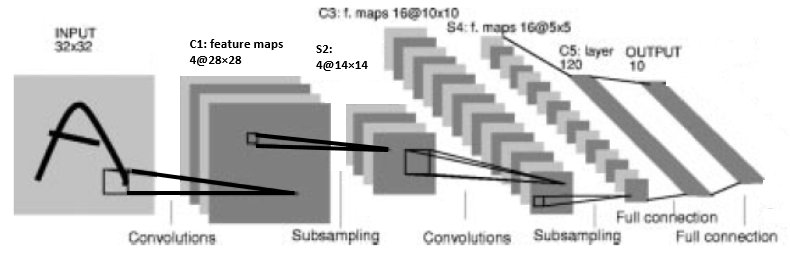
LeNet architecture is the first simple architecture for the convolutional neural network, and it is easy to understand and implement. Yann LeCun proposed Lenet along with Yoshua Bengio, Leon Bottou and Patrick Haffner. LeNet-1, LeNet-4 and LeNet-5 are the versions of LeNet architecture. Here I am going to discuss LeNet-4. LeNet-4 is the updated version of LeNet-1. Picture of LeNet-4 architecture presented below.
Prerequisite:
You have to understand how convolution, pooling and fully connected layer work. Otherwise, you will not understand. You also need to know how to calculate shape. [Click to Know How to Calculate Shape]
The LeNet-4 architecture consists of, two convolution layer, two average pooling layer, followed by a flattening convolution layer, one fully connected layer and one output layer. In this architecture, tanh used as an activation function. The specification of the LeNet-4 presented below layer-wise. Input shape of the image is 32X32. Four 28X28 feature maps in the first convolutional layer by using four 5X5 kernels or filters. Four 14X14 feature maps in the first average pooling layer by using four 2X2 kernels or filters. Sixteen 10X10 feature maps in the second convolution layer by using sixteen 5X5 kernels or filters. Sixteen 5X5 feature maps in the second average pooling layer by using sixteen 2X2 kernels or filters. One fully connected layer of 120 units. Output layers of 10 units. Units of the output layer depend on the number of class. Suppose, ten classes in the dataset then number units in the output layer must be 10.
Now, I am going to explain how to generate outputs in each layer.
Layer 1:
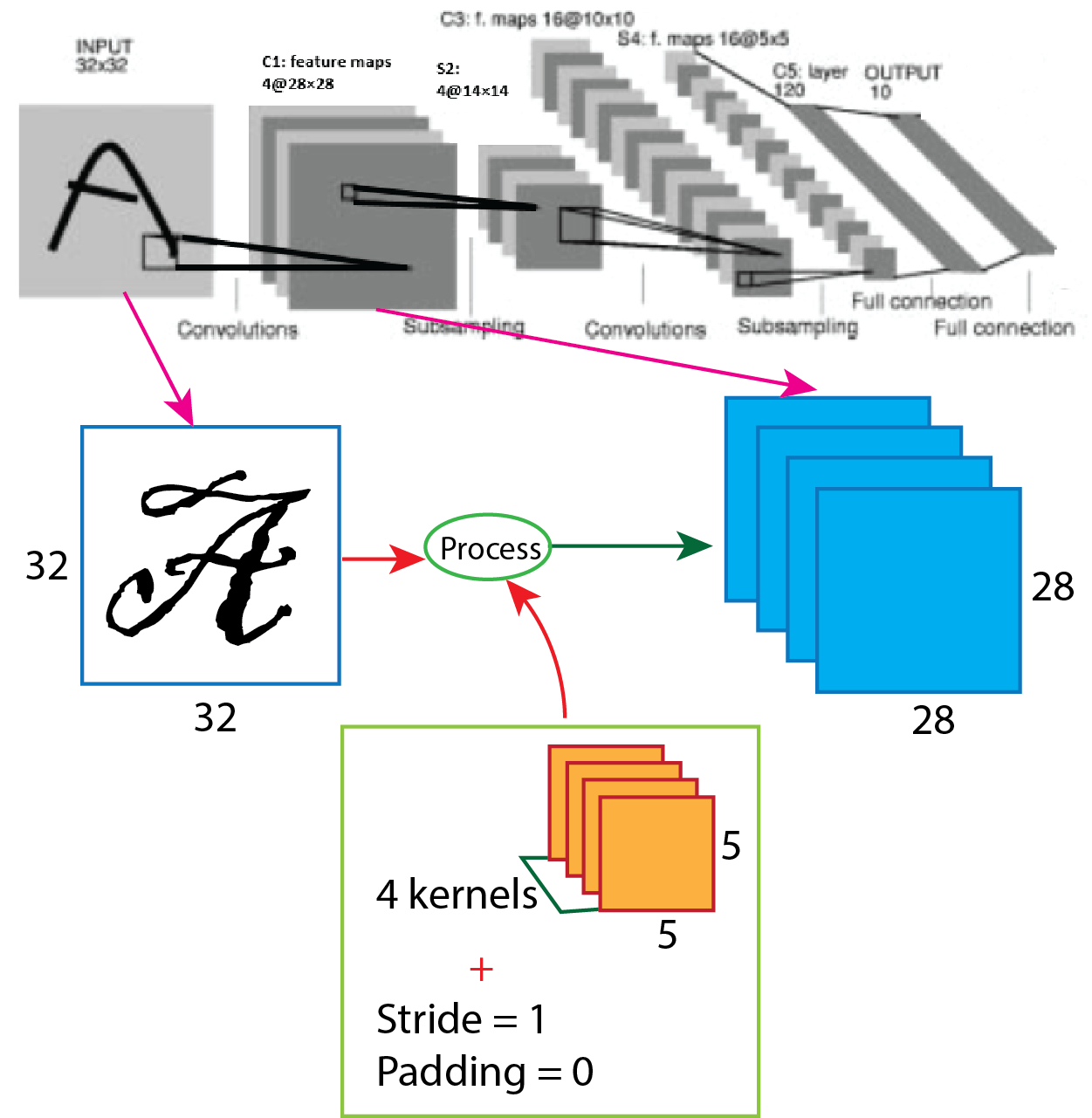
At the beginning of the LeNet-4 architecture, grayscale input image goes through 4 filters having size 5x5 with stride value 1 and the output shape change from 32x32x1 to 28x28x4. For better understanding, a picture of the process presented below.
Now we use an equation to know how the process work which helps to calculate output shape. The parameters for calculation given below:
- Input size 32x32x1 (W=32).
- Total number of kernels or filters 4.
- Single kernel of filter size 5X5 (K=5)
- Number of padding 0 (P=0)
- Stride 1 (S=1)
Now insert all the values in the equation.
So, after the calculation, the result is as same as the image, and the output shape of the first convolution layer turns into 32x32x4.
Layer 2:
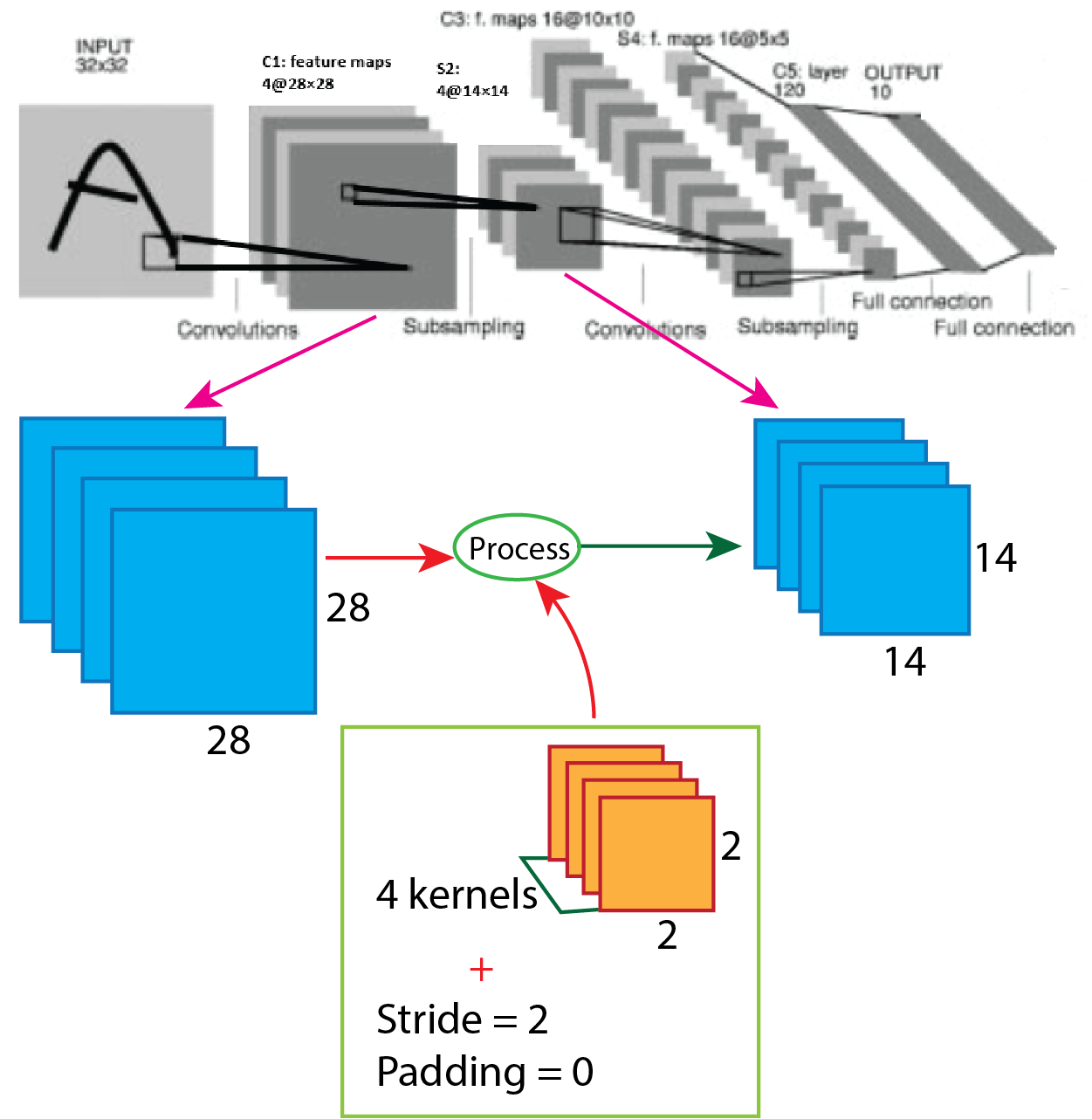
Then in the Lenet-4 architecture, the output of the first convolution goes through the average pooling, and the number of the filter is four having size 2x2 with stride value 2. After applying average pooling output shape change from 28x28x4 to 14x14x4. For better understanding, a picture of the process presented below.
Now we use the equation to know how the process work, which helps to calculate output shape. The parameters for calculation given below:
- Input size 28x28x4 (W=28).
- Total number of kernels or filters 4.
- Single kernel of filter size 2X2 (K=2)
- Number of padding 0 (P=0)
- Stride 2 (S=2)
Now insert all the values in the equation.
So, after the calculation, the result is as same as the image, and the output shape of the first average pooling layer turns into 14x14x4.
Layer 3:
After that, in the Lenet-4 architecture, the output of the first average pooling layer goes through again convolution, and the number of the filter is 16 having size 5x5 with stride value 1. After applying convolution output shape change from 14x14x4 to 10x10x16. For better understanding, a picture of the process presented below.
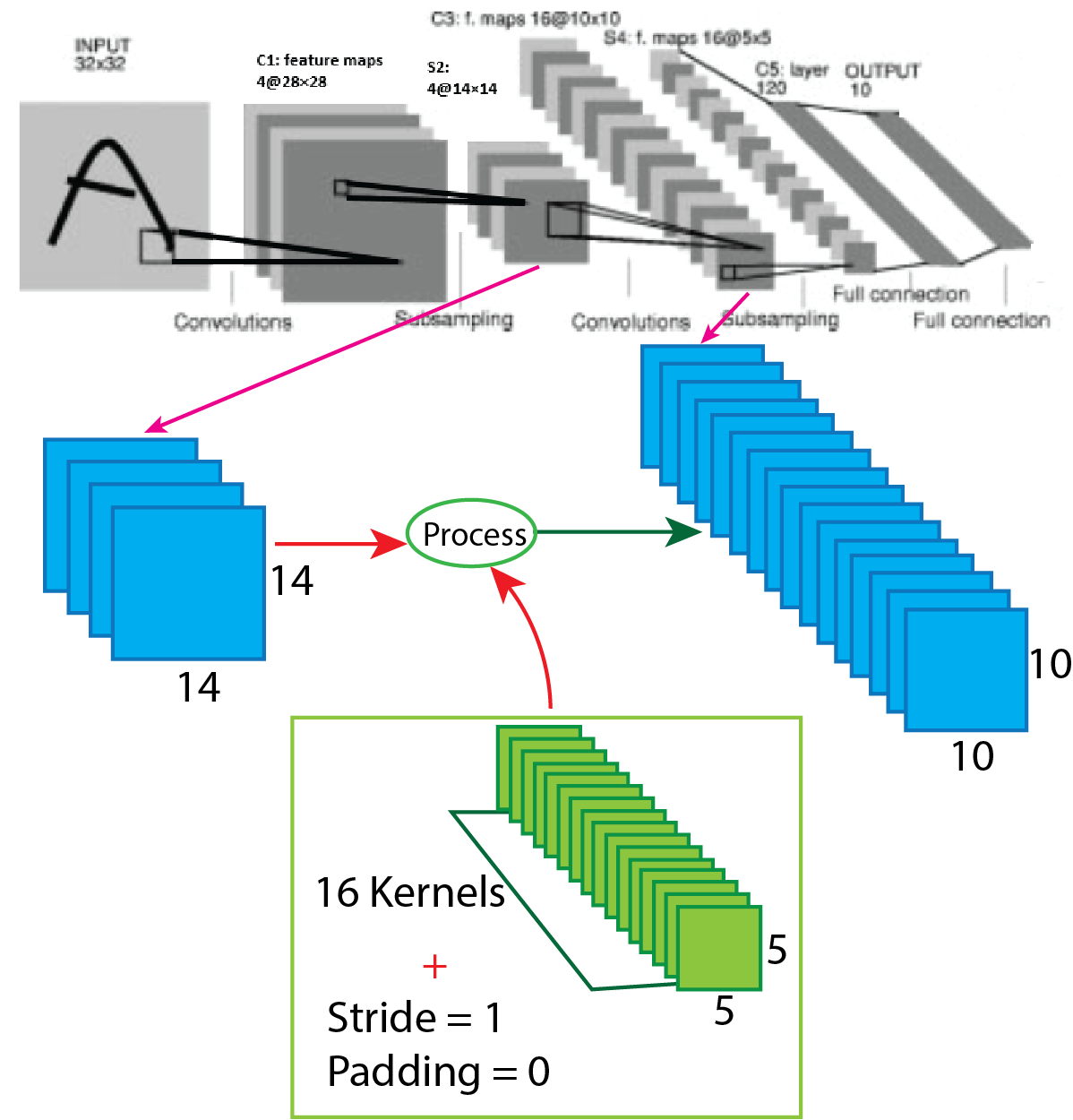
Now we use the equation to know how the process work, which helps to calculate output shape. The parameters for calculation given below:
- Input size 14x14x4 (W=14).
- A total number of kernels or filters 16.
- Single kernel of filter size 5X5 (K=5)
- Number of padding 0 (P=0)
- Stride 1 (S=1)
Now insert all the values in the equation.
So, after the calculation, the result is as same as the image, and the output shape of the second convolution layer turns into 10x10x16.
Layer 4:
After that, in the Lenet-4 architecture, the output of the second convolution layer goes through again average pooling, and the number of the filter is 16 having size 2x2 with stride value 2. After applying average pooling output shape change from 10x10x16 to 5x5x16. For better understanding, a picture of the process presented below.
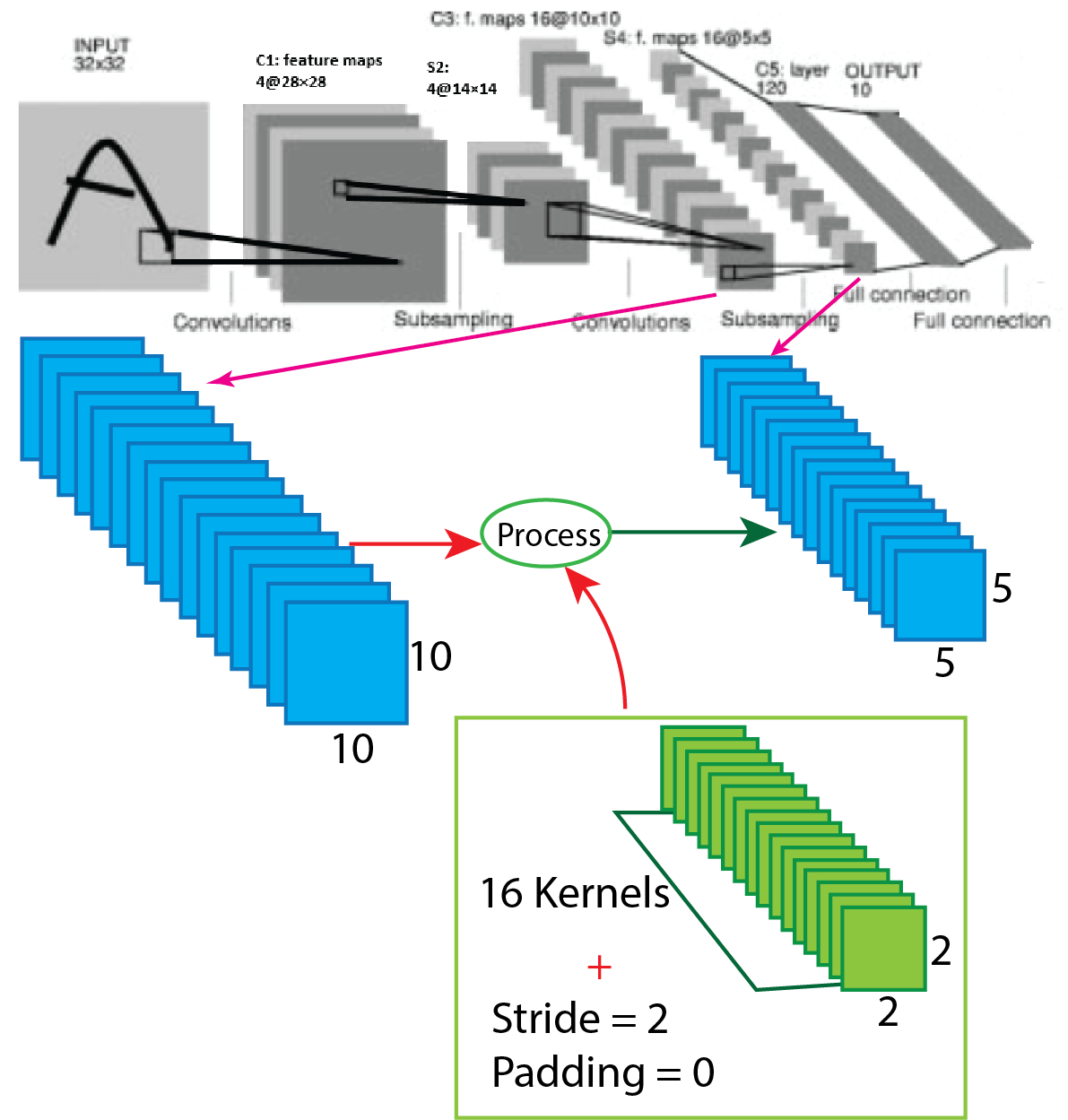
Now we use the equation to know how the process work, which helps to calculate output shape. The parameters for calculation given below:
- Input size 10x10x16 (W=10).
- A total number of kernels or filters 16.
- Single kernel of filter size 2X2 (K=2)
- Number of padding 0 (P=0)
- Stride 2 (S=2)
Now insert all the values in the equation.
So, after the calculation, the result is as same as the image, and the output shape of the second average pooling layer turns into 5x5x16.
Layer 5:
The fifth layer of the Lenet-4 architecture is fully connected convolutional layer with 120 feature maps and each of size 1x1. After the forth layer, the output of the average pooling layer turns into a flatten layer, and that flatten layer connects with the fully connected layer. So, the output shape of the second average layer 5x5x16 turns into flatten layer and shape is 400x1. All 400 neurons or units of the flatten layer connected to all 120 neurons or units of the fully connected layer. For better understanding, a picture of the process presented below.
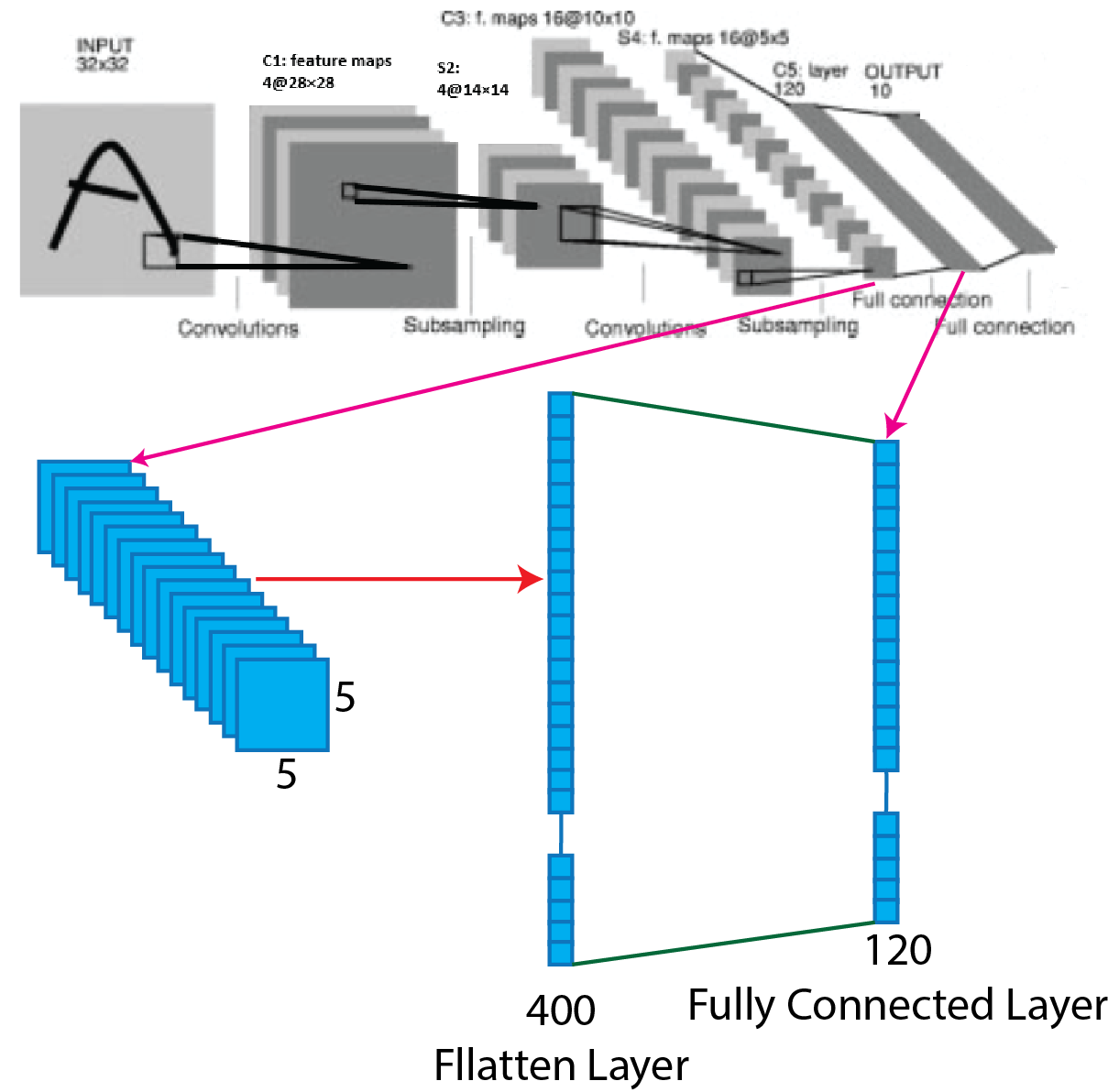
Layer 6:
The final layer of the LeNet-4 architecture is fully connected output layer y shortly output layer with 10 possible values where tanh used as an activation function. Fully connected layer with 120 units connects with output layer. After summation, all the values of the units of the output layers must stay between 0-1. As the LeNet-4 architecture used for MNIST data, that’s why 10 possible units of output layers corresponding to the digits from 0 to 9. For better understanding, a picture of the process presented below.