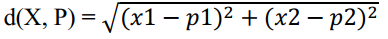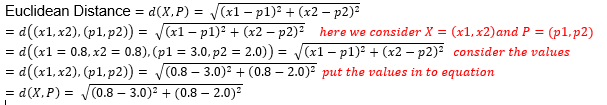Modified K-Nearest Neighbor (MKNN)
This Modified K-Nearest Neighbor is better from traditional KNN in both terms: robustness and performance.
Introduction to MKNN
k-Nearest Neighbor (KNN) classification is one of the simplest and most fundamental classification method like other classification methods. The KNN method should be one of the first choices for classification when there is little or no prior knowledge about the distribution of the data. On the other hand MKNN or modified k-nearest neighbor classification method for enhancing the performance of k-Nearest Neighbor is proposed which uses robust neighbors of training data. Modified K-Nearest Neighbor (MKNN) inspired from the traditional KNN algorithm, the main idea is to classify an input query according to the most frequent tag in set of neighbor tags. MKNN also considered a kind of weighted KNN so that the query label is approximated by weighting the neighbors of the query. The procedure computes the frequencies of the same labeled neighbors to the total number of neighbors.
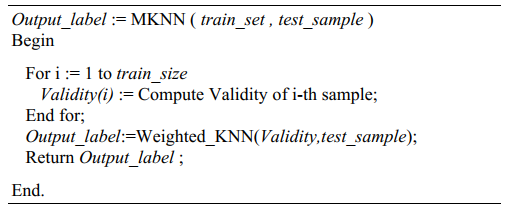
Pseudo-code of the MKNN Algorithm
Let’s understand MKNN in mathematical way:
Consider we have data sets with classes.
| Data set | Class | Data set | Class | Data set | Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 = (0.8, 0.8) | 1 | X2 = (1.0, 1.0) | 1 | X3 = (1.2, 0.8) | 1 |
| X4 = (0.8, 1.2) | 1 | X5 = (1.2, 1.2) | 1 | X6 = (4.0, 3.0) | 2 |
| X7 = (3.8, 2.8) | 2 | X8 = (4.2, 2.8) | 2 | X9 = (3.8, 3.2) | 2 |
| X10 = (4.2, 3.2) | 2 | X11 = (4.4, 2.8) | 2 | X12 = (4.4, 3.2) | 2 |
| X13 = (3.2, 0.4) | 3 | X14 = (3.2, 0.7) | 3 | X15 = (3.8, 0.5) | 3 |
| X16 = (3.5, 1.0) | 3 | X17 = (4.0, 1.0) | 3 | X18 = (4.0, 0.7) | 3 |
There are three classes and they are 1, 2, 3. We consider test pattern P = (3.0, 2.0) and k = 5.
Now calculate the distance between X and P using Euclidean Distance. Here X represents all the data sets from data sheets X1, X2, X3…. X18. P represents the test pattern and k = 5 stands for 5 nearest neighbors.
Euclidean Distance
.
Now, if I write the third formula using data sets and test patterns, it will be looking like this.
Euclidean Distance =
I wish after using the data sets X and test pattern P, someone will not actually understand what’s going on in the formula. Then let’s try with the values of X and P. Here, for the value of X, I use the values of X1(0.8, 0.8) from the data sheet and for the value of P (test pattern), use P(3.0, 2.0).
I wish it’s now understandable for everyone. Now, dig into the mathematics and let’s see test pattern P(3.0, 2.0) belongs to which class. In this example, we have only three classes and they are 1, 2, and 3.
Let’s find the distance between X and P and find the five lowest results because k = 5
Here the list of five lowest results with their class after calculating the distance between X and P. As we consider k = 5 then the nearest neighbor are given below in the list.
| 1st lowest | Class | 2nd lowest | Class | 3rd lowest | Class | 4th lowest | Class | 5th lowest | Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X16 = 1.12 | 3 | X7 = 1.13 | 2 | X14 = 1.31 | 3 | X6 = 1.41 | 2 | X17 = 1.41 | 3 |
Now we consider that,
Class 1 = 0, (Class 1 has no members)
Class 2 = 2, (Class 2 has 2 members and they are X6, X7),
Class 3 = 3, (Class 3 has 3 members and they are X14, X16, X17).
After finishing all the calculation from above, we consider the test pattern P= (3.0, 2.0) and k = 5 then nearest patterns are X16, X7, X14, X6 and X17.
Now applying the weighted KNN,
We know, Class 1 = 0
Class 2 = (X6 + X7) = (0 + 0.97) = 0.97 {note: add all the members value of class 2}
Class 3 = (X16 + X14 + X17) = (1 + 0.34 + 0) = 1.34 {note: add all the members value of class 2}
If we choose lowest result from three classes, then test pattern P(3.0, 2.0) belongs to class 2.
There is a link of a paper on MKNN. You can read this paper for further knowledge. [MKNN: Modified K-Nearest Neighbor]